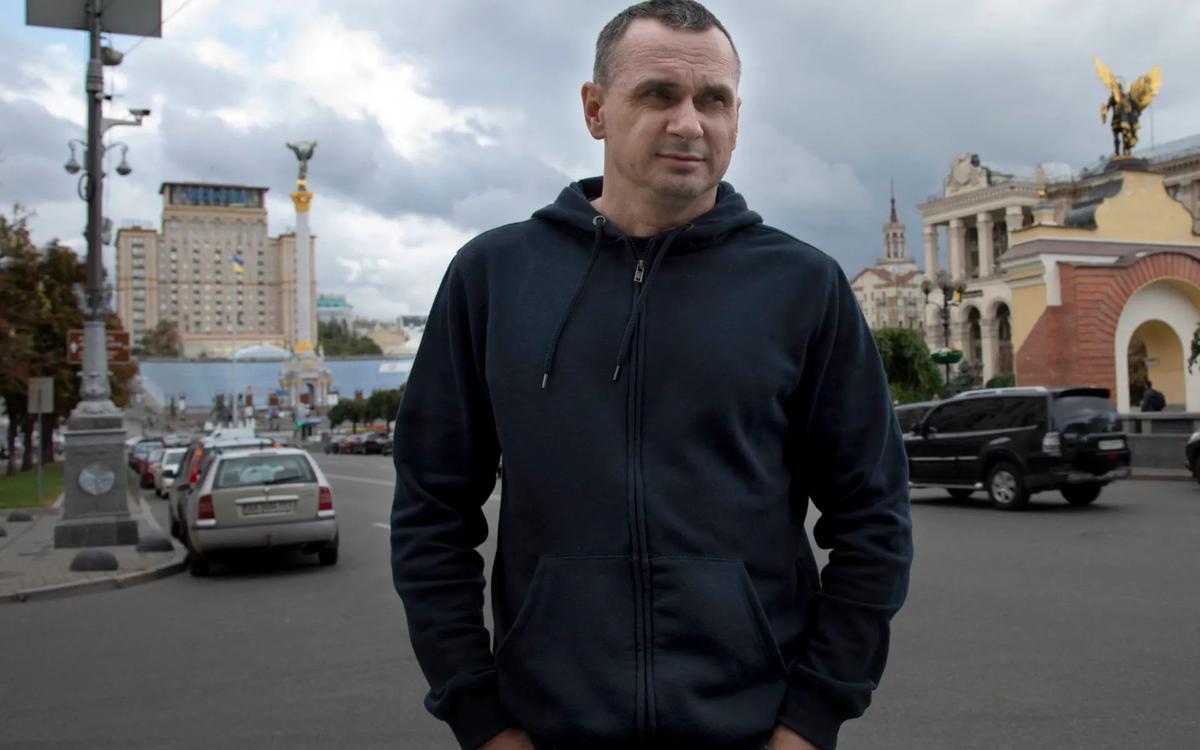
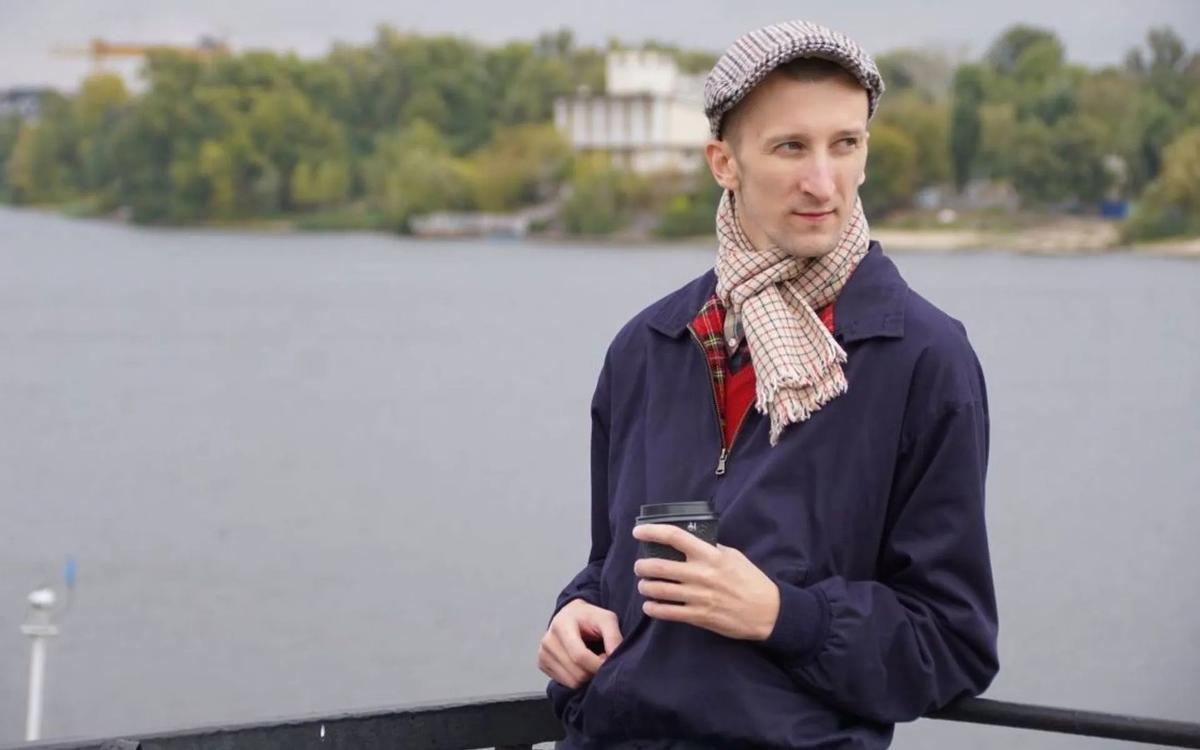
“On your exchange day, we all watched cars with blacked-out windows and security jeeps leaving Lefortovo Detention Center 2 (SIZO-2) and film crews of governmental TV channels gathering at the entrance to Vnukovo… Tell us about the exchange procedure from the first-person point of view?”
“Many people say that the exchange happened unexpectedly but there was nothing unexpected for me. I have been waiting for that for all five years, from the very first day of my detention.
I kept a close eye on the political situation and what the Russian authorities were saying, and everything was heading in that direction. There were discussions about the exchange since the end of May, when it became clear that Russia remains the member of the Council of Europe and is ready to try to establish a dialogue with Ukraine. In view of this, everyone offered to exchange prisoners. Then a press conference with Putin was held, where he was asked a question about the exchange, which speaks for itself because random questions are not asked at such events. Therefore, I understood that the process was already on track.
In September, I began to receive letters with the information that most of the [Ukrainian] guys are already in Lefortovo, and the exchange would probably be carried out soon. I understood that they would apparently change me for Vyshinsky. In the morning of August 28, a prisoner transport vehicle arrived for me. Without any explanations, they brought me to Moscow by plane, and in the evening at Lefortovo I heard on the radio that Vyshinsky was released.
[In SIZO] they told me that the exchange would be carried out and asked me, if possible, to have no contacts with public monitoring commissions and journalists to prevent that everything fell through, because the situation was a bit precarious.
In fact, I had no choice as in addition to asking me not to contact anyone they just did not let anyone in.
“Are you sure that you were exchanged for Vyshinsky, not for Tsemakh(former head of the DNR air defence brigade who was involved in the MN17 crash case.— Ye.R)?”
“I’ve learned about Tsemakh, being already on the board, from the Assistant to President. He asked me, ‘There is an opinion that you were against this exchange’. I said, ‘What do you mean? It's the first time I’ve heard this name. Who is it?’ ”
“On August 28, you were flying to Moscow, having already realized that you were released. What did you felt?”
“I felt nothing. For nine days at Lefortovo, I was not nervous, I slept calmly. I was absolutely calm until I got out of the plane and saw my daughter.”
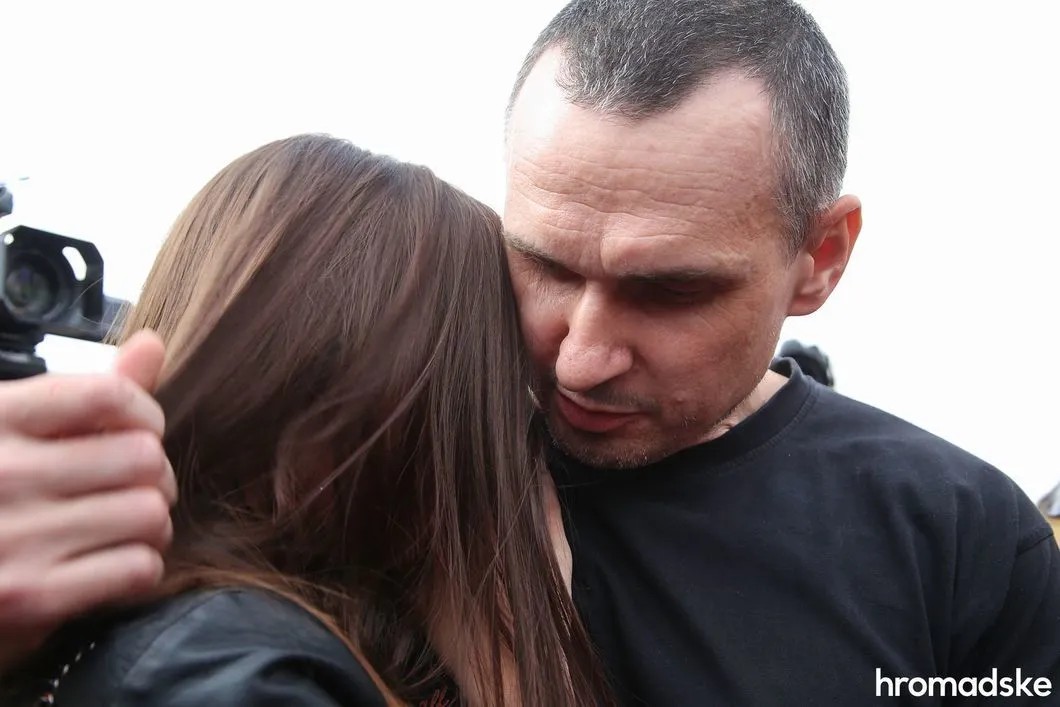

“When did you felt that everything was over and you were free?”
“I can’t recollect such a moment … I didn’t felt at all that I wasn’t free. I lived there, now I live here. Nothing has changed inside me, nothing has snapped.”
“Didn’t you really felt that you were in prison?”
“From the first hours of my detention, I had a feeling that the situation was serious and I was to stay there for long. I refused to cooperate; they found nothing during the personal search, and I told them [the FSB officers], ‘Well, guys, is it all up? Can I go?’ They said, ‘No, you’ve had it, you can’t leave us that easy.’
So the case was slowly growing. They caught me but didn’t find anything except a testimony against me, which was poor and vague. Then they began to supplement the testimony for the sake of the investigation. They just fabricated the case against me. Not against me, Sentsov, personally, but against the brigade. It just so happened that I headed it. It didn't matter to them if it was me or Serebrennikov… A random choice. We are all sludge for them, they would trample us and won't even notice. They worship Putin and don’t care about the rest of people.
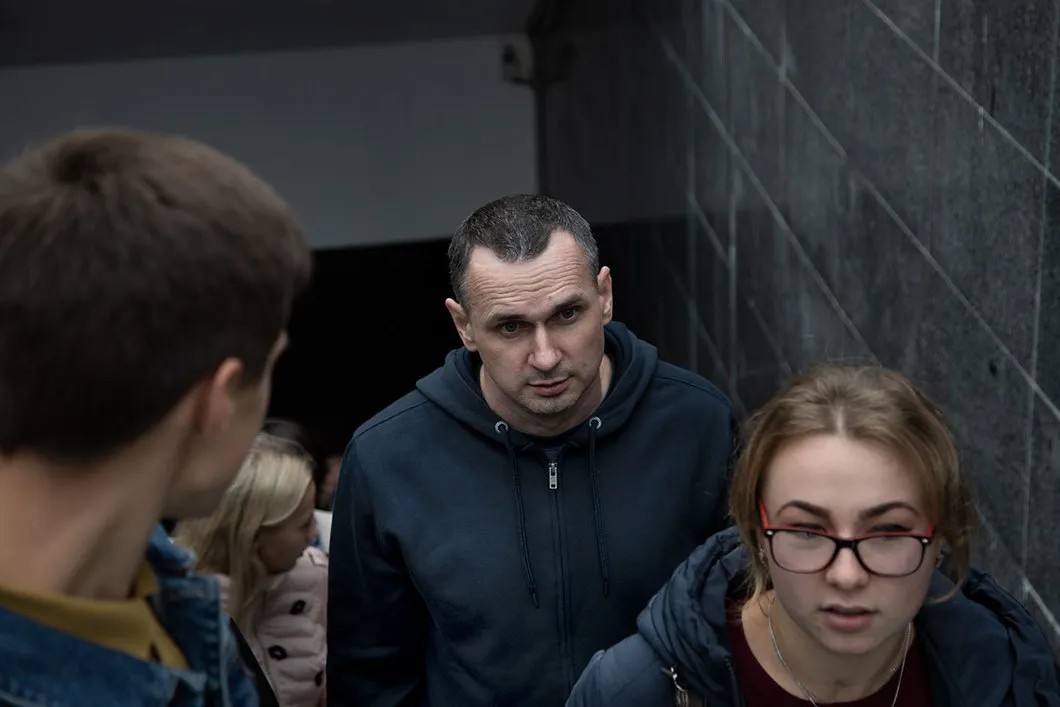

When the investigation was already over and I was to be transferred to Rostov for trial, I was left face to face with the chief investigator. We had just a minute as the convoy was to come for me in a moment. Realizing that we would never see each other again, he asked, ‘Well, will you testify in court?’ I said, ‘No, I won’t, what’s the point?’ ‘It would be interesting to hear what had really happened.’
I was struck that he really understood that everything he had fabricated was total garbage. You know, how they [investigators] think. The field investigator believes that since he caught you, he has to squeeze a confession from you. The investigator thinks that you are not to blame, but are dangerous for the state, so you must be imprisoned. The judge understands that the evidence is false, but the investigators can’t accuse somebody without a reason, so, since this is a requirement of the state, you must be imprisoned. They just do their job, nothing personal.
Once, when everyone went out during the search, one police officer stayed with me and said, so humanly, ‘I pity you but there’s nothing to be done.’
“Was it often that SIZO and camp officers employees were sympathetic to you?”
“I can remember a single case. I was going in a prison van when a young security guard said, ‘I read, watch, and support you.’ There was no more sympathy and no particular malice or cruelty as well. I had a red stripe (a mark in the prisoner's documents that he was prone to escape. — Ye.R.) assigned to me in Labytnangi. Every two hours during the day they came to the hut and checked me, and every two hours at night a patrol came and shone a light in my eyes. Some just shone for a second and went away and some were shining in my eyes until I woke up. I realized that there were not so many bastards as one could think. Physical force was never used there, but I faced an attempts to humiliate and morally trample me at every turn. The lower the position, the more an officer is unaccountable and free in his actions.
A colonel cannot afford himself to use foul language while a sergeant can do anything, often at his own initiative, just because he is ‘for the Russian world’, and you are a ‘banderovets’.”
“Do they really think so? Does propaganda work?”
“Absolutely.”
Accusation
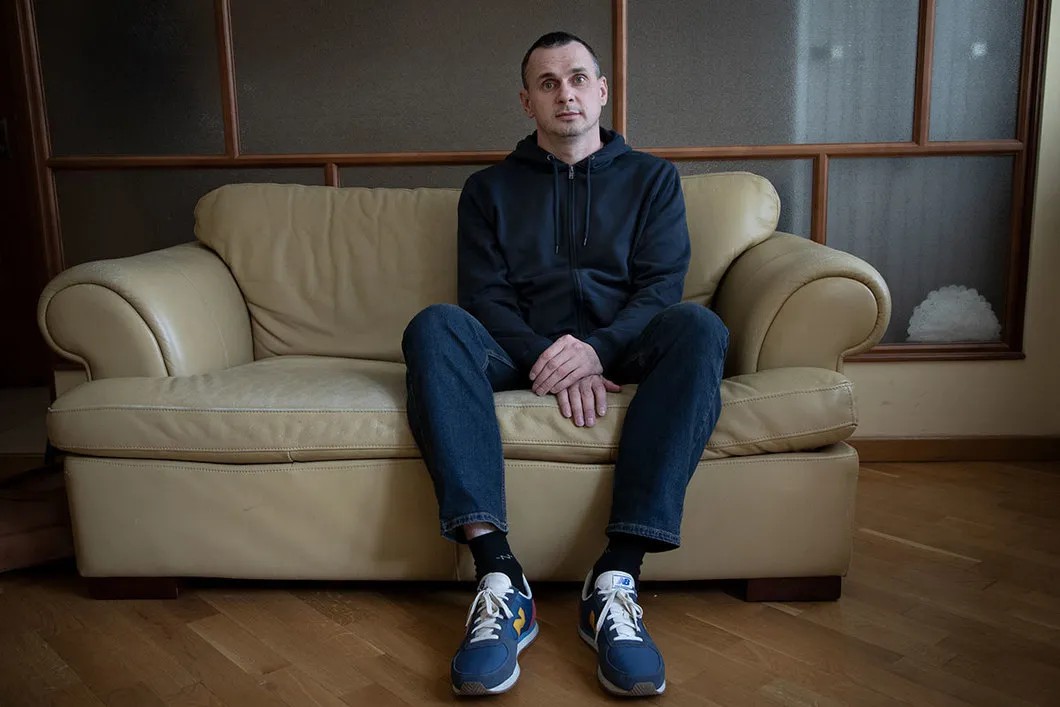

“Like the investigator you’ve mentioned, I wonder if anything of what you are accused of has really happened?”
“I have nothing to hide. There [in Crimea] was chaos. Attacks, troops, disappearing people… There were a lot of meetings and conversations. We were offered crazy things: let's form partisan units, let’s go into the woods.
That was proposed by people who had no experience of the kind at all! After having been at the Maidan and participated in street battles face to face, I looked at them and thought, ‘You are just children, who don't know what they're doing.’
Everyone did what he could: someone pulled off Russian flags, someone broke a window, someone set fire to the door of the Russian community of Crimea… This was a hooligan act, not significant even for the police. A case was opened pursuant to Article 167 of your Russian Code (the Criminal Code, “Intentional Destruction or Damage to Another's Property”). It was almost a dead end.”
“Did you participate in those events?”
“No, I didn’t. I am for Ukraine, I am against Putin's Russia and I will fight as best I can, but I do not support actions directed against health of other people, even if they are military officers. While they don’t shoot at us, we have no right to shoot at them.
Then shortly before the presidential election in Ukraine, a command was issued to demonstrate that Ukraine was aggressive and wanted to blow up Crimea, in order to show the Crimeans the “threat” and persuade them that they were saved. They began to search and detain people. They found Chirniy (Alexey Chirniy, a Crimean historian and one of Sentsov’s sidekicks, admitted himself guilty and entered into a pre-trial cooperation agreement.He was sentenced to seven years in prison.— Ye.R.) and began to spy on him and wiretap his conversations. They detained him, brought to the basement and tortured, and he agreed with everything. However, it’s his fault as he in fact was stuck to Nazi ideas. I saw a video with him wearing the Bundestag uniform. Neither me, nor, for example, Sasha Kolchenko, an anti-fascist, could have anything in common with this person, we even didn’t know each other.
Then they detained Afanasyev (Gennadiy Afanasyev admitted himself guilty, cooperated with the investigation, and gave testimony that formed the basis of the allegations of Oleg Sentsov and Alexander Kolchenko, but later refused it, saying that he had given it under tortures. — Ye.R.). I talked with him several times, we saved a couple of guys and took them out of Crimea. People often disappeared at that time: two of my friends are still missing. Vasya Chernysh (a resident of Sevastopol, an activist of Avtomaydan, a former employee of the Security Service of Ukraine, and a member of the Ukrainian resistance in Crimea. Disappeared on March 15, 2014.— Ye.R.) and Timur Shaimardanov (a resident of Simferopol, an activist of the Ukrainian People’s House, and a resistance coordinator in Crimea. Disappeared on May 26, 2014.— Ye.R.). When Afanasyev was detained, I did not know who and for what had grabbed him but I had to find out what was happening to him and help. Then he began to call me and I realized that I was also under pressure, that they were also searching for me. I had an opportunity to leave for more than a day, but I did not leave because I wasn’t involved in any illegal matters. Many of the Avtomaydan participants were detained, beaten and released because they couldn’t produce anything against them. The pro-Ukrainian position is not enough for the accusation so I didn’t feel anxious, but I took security measures and moved to another place, but they managed to detect me from my car location.”
“At the court session, you told that you were tortured during the interrogations.”
“Everything that was made to me has already been described. There are people who have experienced a lot more. In prison, every second person is interrogated in the same way as me or much worse. This is how the system works. Because of so much attention paid to me, I don’t want to talk about it… Did you read about Pshenichniy (Valeriy Pshenichniy, who was involved in the case of embezzlement from the Ministry of Defense and tortured to death in prison.— Ye.R.)? That's who we must talk about. Not me.
“And what about Kostya Kotov?”
“I don't know him personally. There are guys who just do their job and nobody knows them. For example, I do my job in Crimea: I take out the military. I was asked by a commander, ‘What’s your name? Everybody left us but you took us out. Who are you at all? Why are you doing this?’ ‘It doesn’t matter. Have a safe trip!’ Kostya and many others just did their best and didn’t brag. I feel a soul connection with him because I’m the same, I just do my best and don’t brag.”
“He killed somebody for the cause but I was a terrorist”
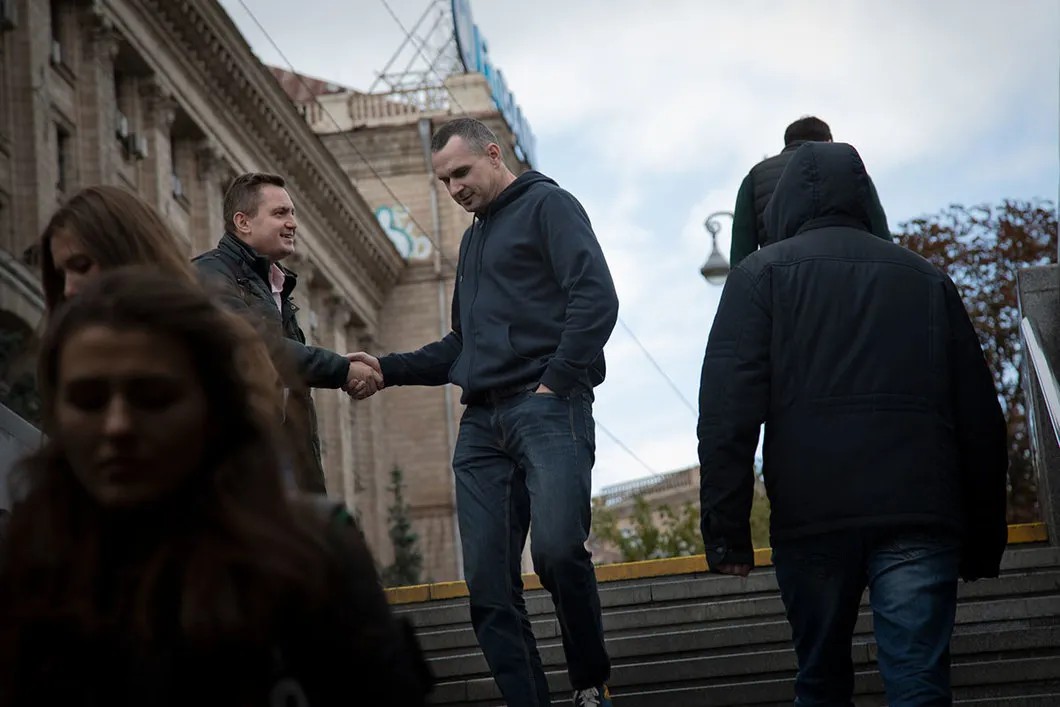

“What was your relationship with the prisoners?”
“I was kept in small huts accommodating 50-60 people. They were ordinary guys. Some were just unlucky, some got to prison by chance, some were usual visitors of police juvenile rooms since their childhood. Most of them are not interested in politics, they don’t care and watch Muz-TV, TNT… Of the others, the minority supported me but the majority was against me. But there are unwritten prison laws that prohibit harassment. I had no problems with that. However, I was in the aggressive environment all the time. They treated me as a stranger, as an enemy who had come to their place.”
“Do you mean that, for example, a guy who had killed somebody with an ax being drunken was treated better?”
“Of course. He killed somebody for the cause but I was a terrorist. Nobody said that directly, but I felt the oppressiveness like high atmospheric pressure.”
“At the last court session, you said that you met in prison militia and a GRU officer who fought in Donbass. How did you meet them?”
“I met the GRU officer in a Rostov court where his case was heard in parallel with mine. He participated in the Crimea invasion and Illovaisk battle, shot at my fellows. I didn’t hate him. Prison like death, makes us equal. I was interested to hear from him the truth about those events. I was astonished when I learnt that they transported military boats from Novorossiysk to Sevastopol on March 24, three days before the seizure of the buildings [of the Supreme Council and the Council of Ministers of Crimea]. The operational plan for the Crimea invasion was developed for a few days. And second, ‘During the Illovaisk battle,’ he said, ‘we did all the main things. We didn’t contact the militia.’ All the main battles of 2014 that caused damage to the Ukrainian army were conducted by the Russian army.
The militia was weak, and if Russia had not intervened, had not sent its troops, the DPR would have already been knocked down by the fall of 2014.
I talked to the man who told this straight forward. He had no reason to lie because he was going to prison.”
Поддержите
нашу работу!
Нажимая кнопку «Стать соучастником»,
я принимаю условия и подтверждаю свое гражданство РФ
Если у вас есть вопросы, пишите [email protected] или звоните:
+7 (929) 612-03-68
“Wasn’t he imprisoned for war crimes?”
“It was a domestic. GRU officers are accustomed to killing. He met a policeman who said something sharp to him, and he just killed him.
Regarding the militia, I met them during the transportation of prisoners. One of them fought for money. He was completely insane, once tried to hung himself, then slashed his wrists. The other was a nice home-grown boy of the same age, about 21-22 years old. He was wanted in Russia for extremism and in 2014 came to Novorossia to build the new Russia, independent of the old Russia. Of course, he received a good dose of reality during the year. I asked him, ‘For how long have you been fighting?’ ‘I have fought in a battle.’ ‘What battle?’ ‘They shot at us, we ran.’ The rest of the time they were guarding something.
Everything took place under Russian supervision. He was shocked to realize that he had been against Putin but it turned to be that he was for him in fact.
I asked him, ‘Remember 2014, all the battles, regular army. How could you resist?’ ‘Well, we had more stuff: more tanks, more ‘grads’, more artillery. Of course, we could not be defeated.’ Where did all this come from? He understood. Then he went to Rostov to hang out, got drunk somewhere and was taken to the police, where they found out that he was wanted. That’s how he went to prison. I didn’t hate him. Such a gosling, should I have beaten him for that or what?”
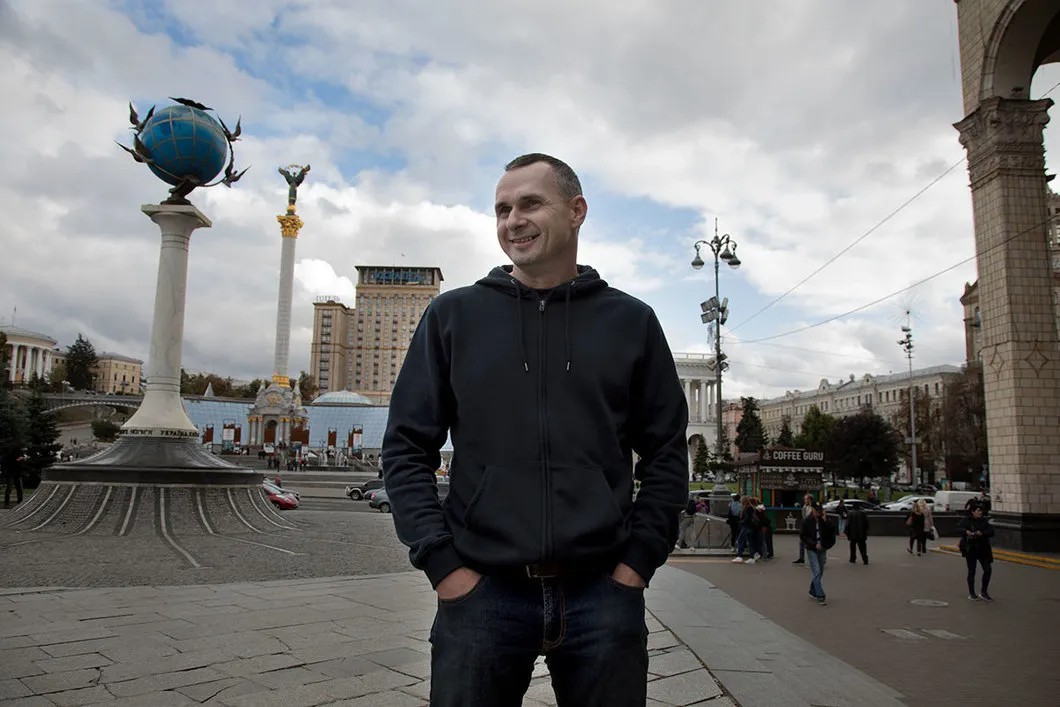

“At the first press conference, you said that you had been arrested two days before you were supposed to leave for Donbass?”
“Yes, this is true. I was at the Maydan for two months; when it was all over, I spent a week at the Avtomaydan headquarters as there was a lot of administrative work. As soon as I started to clean all up, I saw on TV that the Crimea invasion had begun. Many did not believe that was a serious affair. Half of the country then was in the mess: Odessa, Kharkov, Donetsk, Dnipro.
I understood everything and said to my fellows that I was going home: the mess began. I arrived two days later [after the seizure of the government buildings] and immediately got into the work: communication, coordination…
I can’t say that I took over the command, but I did all I could, and, as it then turned out, I had done a lot. And in late April – early May, it became clear that the Donbass was getting heated. Nothing could be done in Crimea, we had lost it. And I decided to go there. I had friends in volunteer battalions and planned to join them, even managed to buy a ticket to Kiev. The found it [during the arrest] and said, ‘So you’re trying to escape!’ That’s how I didn’t get to the war but got to prison instead.”
“Feeling like you are gone”
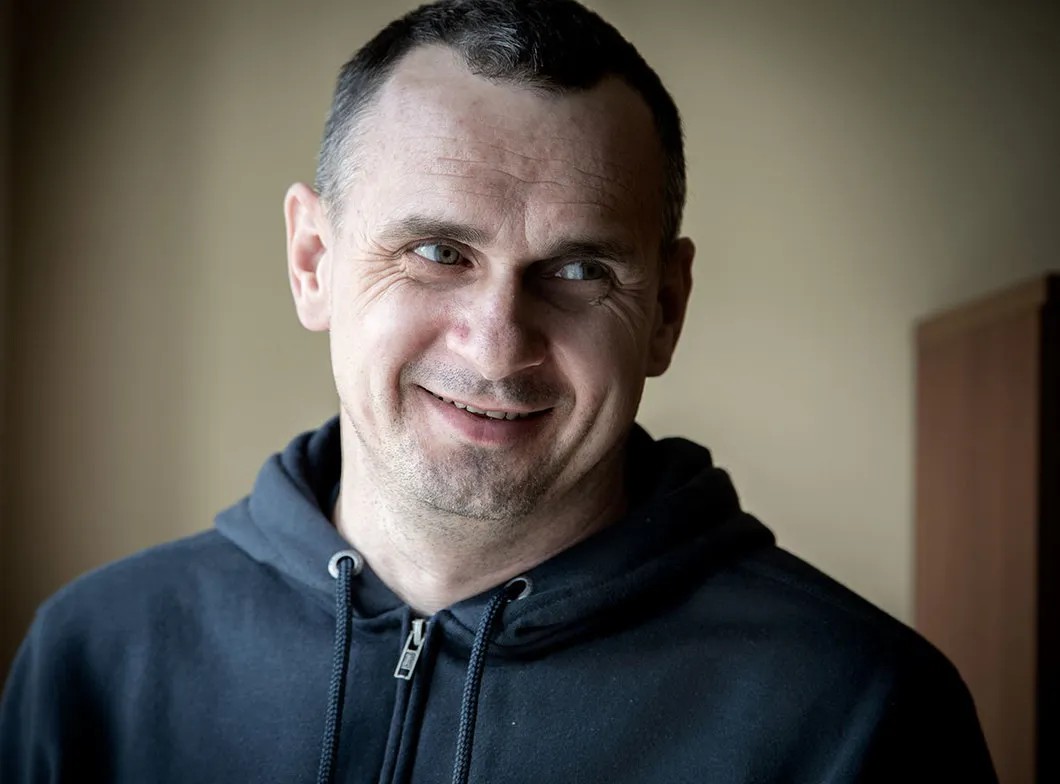

“When you went on a hunger strike for an indefinite term in May 2018, we talked with Natasha Kaplan [Sentsov’s cousin]. From conversations with you, she took the hunger strike as a well-prepared, deliberate suicide.”
“If I wanted to commit suicide, I would find much faster ways. I understood that a hunger strike was an inefficient way, that it would not change anything, but that was the last thing that I could do. It was not a death wish, I love life.”
“Did you believe that your demand to release all Ukrainian political prisoners will be met?”
“Of course, I didn’t. But what could I do? My goal was to attract as much attention as possible, not only to myself but to all our fellows. [Thanks to the hunger strike] they began to write more about us, I think it was a contribution that helped us get out. I understood that I risk more health than life. They wouldn’t let me die, but I could lose my health.”
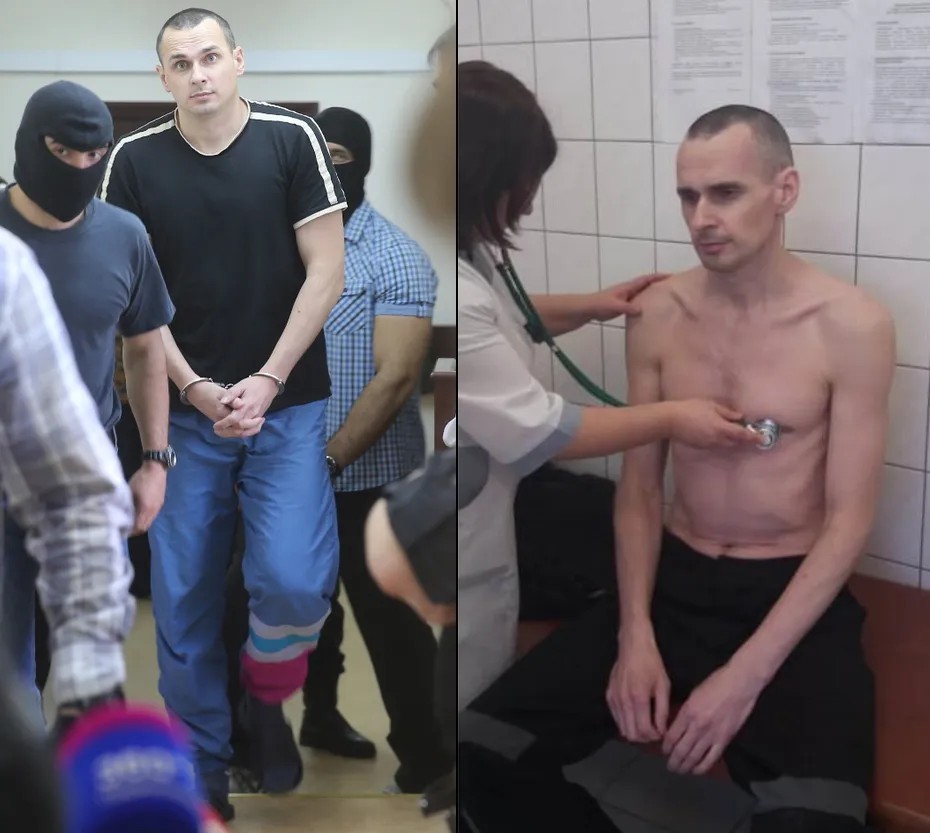
“How did doctors treat you in the municipal hospital?”
“I am grateful to the medical personnel of the prison camp who treated, helped, and saved me. Thanks to their work, I preserved my health. I was like in a real oasis. The military officers pressed on me, sometimes softly, sometimes severely, to make me give up. And the medical personnel was not so tough, they seemed to be trying to give me a little air.
In prison, doctors are accustomed to prisoners, they understand that we are the same people as everybody else. And for doctors at the Labytnangi municipal hospital, I was just a prisoner. They are even not familiar with your case but they see you in your prisoner's robe and that’s all, you are an outcast for them, a convict.
They didn’t want me to die, but they treated me simply: let's get him here, now we’ll stuff a probe in his ass, everything will be fine.
‘You are dying. Three days later you’ll find yourself in the morgue. Give up!’ I kicked that off. I thought that if I was to die, I should die in the Federal Penitentiary Service. It was like to detonate a grenade in the enemy trench. So I did all I could to stay in prison.”
“How did you decide to end up your hunger strike?”
“145 days of hunger is a hard challenge, even with medical nutrition. At the end of the hunger strike, I felt that I was really dying. In the mornings, my upper blood pressure value was 40 and lower pressure was absent. You get used to it physically, it was difficult physically during the first and last months. And it was morally difficult all the time, because you are feeling like you are gone. Avolition and absolute weakness, month by month. The doctors showed me my medical documents – I was already familiar with cardiograms, ultrasound cards and so on – there were problems with my heart, my kidneys which were clogged, and my liver. The doctors said, ‘That’s all, if you don’t give up now, then you won’t be able to eat any more.’ I saw from my medical documents that they were right, one of my legs was almost dead. It was a matter of days.”
“Did you know how people outside supported you?”
“I knew. I read The Novaya (the editorial staff subscribed Sentsov to the newspaper, and he received it most of the time.— Ye.R.). But it’s still difficult for me to understand the scale of their support … I can see it from the reaction of people, many people recognize me on the streets, call and write me. But then it seemed to be hardly relevant to me, as if I had a namesake on the outside. Now I’ve got already used to feel that I’m that guy.”
“In the interview, you said that you thought about the second hunger strike in May of this year. Did you want to re-draw attention to political prisoners?”
“Well, what if there is no other way? I was preparing for a hunger strike, but then the presidential election was held, Zelensky won, negotiations on the exchange were commenced, and I realized that the stupidest thing I could do at the moment was to intervene.”
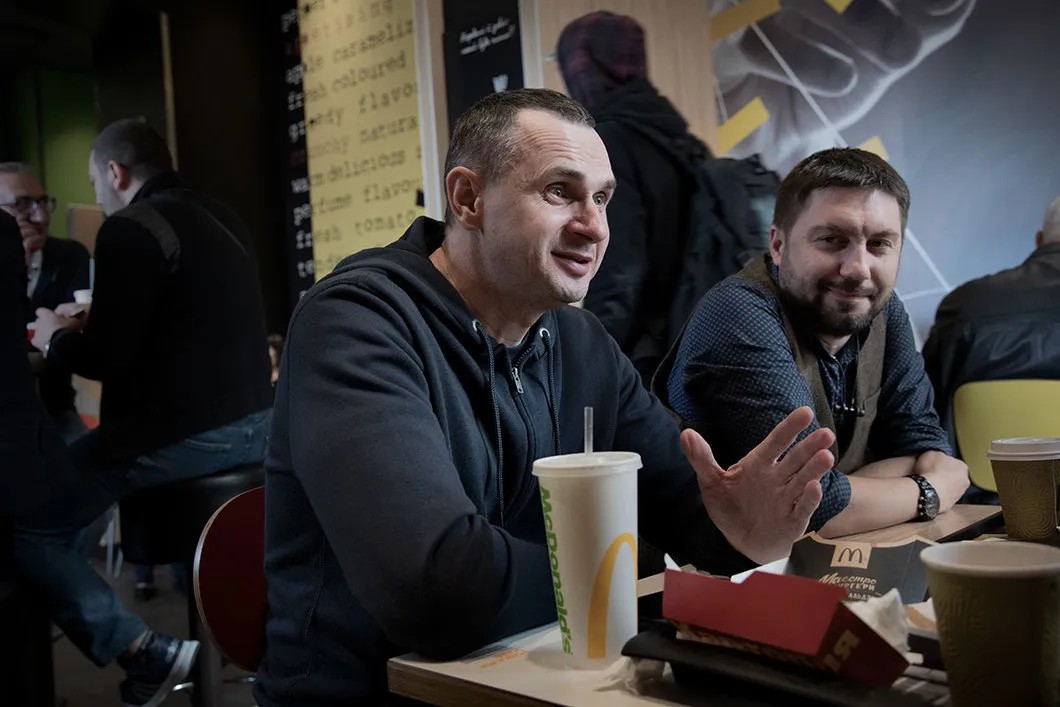

“Natasha Kaplan said that you refused to meet with your relatives?”
“It was just easier that way. My children are small and my mother is ill. It was hard for them to get there, physically. Moreover, it was hard emotionally. Imagine, you see them and have to part. How to keep living after that? It’s easier not to see them at all.”
“I have no home in Crimea any more, it has been taken away by enemies.”

“Are you going to participate in the campaign for the release of political prisoners?”
“I’m obliged to tell about them. I’m not a human rights activist, I’m an organizer, I’ve been working with people and processes for all my life. I wasn’t interested in protection of human rights, but now I am engaged in social activities, it had to be this way. I can’t lay low and say, ‘All right, everybody, I am out of here.’ I’ll do everything I can for my country, to fight the Putin's regime, and to support political prisoners. I won’t have enough time to do something specific such as to bring food parcels or to keep track of particular people. I’ll do it at a different level. I’ve already scheduled trips around the world until the end of the year. The meetings will be held at a serious level.”
“Can you give some examples?”
“It doesn’t matter. I don’t like to tell about my plans. I’ll do what I consider necessary, I’ll do my best. But this will not be work aimed at human rights protection, it will be social work related to political prisoners. All political prisoners. I won’t make this personal and go into details because then I won’t be able to do big and important things. I will take a piece for myself and will do my best without spreading too thin.”
“You got out of prison to another country, another city…”
“You’ve put the question incorrectly because you know little about my life. I lived actually between two cities. I have long felt suffocating in Simferopol, it was too muggy, stuffy for me. I’ve outgrown this city a long time ago and, having got out of prison, I returned home, to Kiev. I have no home in Crimea any more, it has been taken away by enemies.
This split has separated my friends, my relatives. Many people from my social circle have already left Crimea because it is stifling there, it has turned into a prison like the whole Russian Federation.”
“Shalamov wrote that the camp experience is completely negative while Solzhenitsyn considered it as an invaluable challenge. What is your experience like?”
“The problem is not prison as such but your attitude to it. The prison hammers every second into mess. I saw how people drove themselves just to the point just for six months. Prison was not so hard challenge for me as for others. Maybe I'm not so impressionable, maybe I was better prepared. I felt … I won’t say comfortable, but calm. It wasn’t a catastrophe. Regarding my camp experience… I’d say that any experience is good.
I had to serve and I served. I’ve lived this period of my life properly.”

“What did you do in prison?”
“I read a lot, wrote a lot, I’ve used up 15 notebooks. I kept the diary of my hunger strike, wrote five scenarios, of which three have already been completed, two novels, two storybooks, plus some notes… They say that I'm talking in quotes. I say something and it goes to the people. I even write in quotes. I can write a book of quotes. Maybe I'll publish it someday. I also learned English. I did physical exercises. I try to support myself physically. Everyone saw me going out and said, “He is in such a good shape!” [after the hunger strike]. But I did not lie on the couch for a year, I exercised in order to protect my health and prepare for a new hunger strike.”
“Have you changed personally for this time?”
“Everybody would change for five years. Someone [in prison] is just sitting and looking at the ceiling, someone drinks “toilet wine” (“chifir”). There are people who are self-developing. They are rare but still they are there. I’m one of them.
I haven’t lost a single day in prison, I haven’t been bored a single day. I don’t regret these five years.
In the past, I used to be a more aggressive, tough person. They say that now I’m a sharp man – they just haven’t known me before. I do not consider myself ideal, I constantly work on myself. This process didn’t stop in prison.
All my friends were afraid that the prison would change me, harden me. But having talked with me, they said, ‘He hasn’t changed.’ ”
Yelena Racheva, photo by Anna Artyomyeva, Kiev
Поддержите
нашу работу!
Нажимая кнопку «Стать соучастником»,
я принимаю условия и подтверждаю свое гражданство РФ
Если у вас есть вопросы, пишите [email protected] или звоните:
+7 (929) 612-03-68

